Data storage is an essential component of modern computing systems. From personal computers to large-scale data centers, efficient and reliable data storage solutions are required to manage the ever-increasing amount of data generated by various applications. One such solution is the DAS storage system.
DAS, or Direct-Attached Storage, is a type of storage system that directly connects to a host computer or server without the need for a network. In other words, the storage device is physically attached to the host system, usually via a cable, and the data is transferred directly between them.
Benefits of Using the DAS System
DAS (Direct-Attached Storage) is a commonly used device. Businesses rely on this system due to its many benefits. Nevertheless, it is always essential to consider the drawbacks of the system as well.
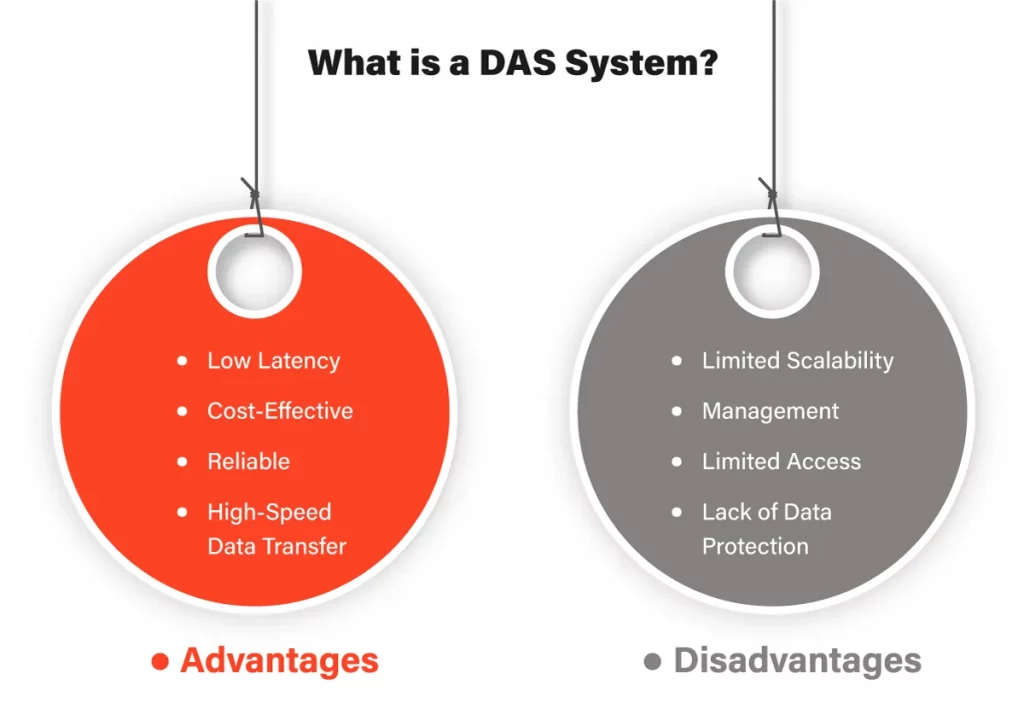
Advantages of DAS Systems
- High-Speed Data Transfer. DAS storage systems offer high-speed data transfer rates, making them ideal for applications requiring quick data access.
- Low Latency. Since DAS storage systems are directly attached to the host system, they offer low latency and are less prone to network-related issues such as congestion and packet loss.
- Cost-Effective. DAS storage systems are generally easy to install and manage, making them a cost-effective solution for small-scale storage needs.
- Reliable. DAS storage systems are reliable, as they are less affected by network-related issues and less prone to failure than network-based storage solutions.
Disadvantages of DAS Systems
- Limited Scalability. DAS systems are limited in scalability, as they are designed to be used with a single host system. This makes them unsuitable for large-scale storage needs.
- Management. DAS storage systems require manual management, which can be time-consuming and complex for large-scale deployments.
- Lack of Data Protection. DAS does not offer data protection features such as RAID, which makes them vulnerable to data loss in the event of a hardware failure.
- Limited Access. Since DAS systems are directly attached to a single host system, they offer limited access to data. This makes them unsuitable for applications that require shared access to data.
Types of DAS Storage Systems
There are several types of DAS storage systems available in the market, each with its unique features and advantages.
Hard Disk Drive (HDD) DAS. This is the most common type of DAS storage system, based on traditional hard disk drives. It is relatively inexpensive and offers high storage capacity. However, it is slower than other types of DAS storage systems and prone to mechanical failures.
Solid State Drive (SSD) DAS. SSD DAS storage systems are based on solid-state drives, which use flash memory to store data. They offer higher data transfer rates and lower latency.
In addition, they are more reliable than HDD DAS storage systems. However, they are more expensive and offer lower storage capacity compared to HDD DAS systems.

Network-Attached Storage (NAS) DAS. Network Attached Storage (NAS) DAS systems are designed to provide network access to DAS storage devices. They offer the benefits of DAS storage systems, such as high-speed data transfer rates and low latency, while allowing access to multiple users over a network.
However, they are more expensive and complex to manage compared to traditional DAS storage systems.
Storage Area Network (SAN) DAS. SAN DAS storage systems are designed to provide block-level access to storage devices over a network. SAN DAS offers high-speed data transfer rates, low latency, and is highly scalable. However, they are complex to set up and manage. Moreover, these systems require specialized hardware and software.
Where DAS Storage Systems are Used
DAS storage systems are used in various applications, from personal computers to large-scale data centers. Some common applications of DAS storage systems include:
- Video Editing. DAS storage systems are widely used in video editing applications. They offer high-speed data transfer rates and low latency, allowing editors to work with large video files in real time.
- Gaming. DAS storage systems are also used in gaming applications, where they offer fast loading times and quick access to game data, improving the overall gaming experience.
- Small-Scale Data Centers. DAS storage systems are also employed in small-scale data centers, offering a cost-effective solution for storing and managing data.
- Backup and Recovery. DAS storage systems are also used for backup and recovery purposes, allowing organizations to easily back up and recover data during a hardware failure.
DAS storage systems are an important component of modern computing systems, offering various advantages for their users. While they are unsuitable for large-scale storage, they are ideal for small-scale storage requirements and are widely used in different fields. When choosing a DAS storage system, it is important to consider factors such as the type of storage device, data protection features, and management requirements to ensure that the system meets the specific needs of the application. After considering all these factors, you can choose the most suitable option for your needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Direct Attached Storage (DAS)?
Direct Attached Storage (DAS) refers to a storage architecture where storage devices are directly connected to a host system, such as a computer or server, without the need for a network infrastructure. DAS provides dedicated and exclusive access to storage resources for the host system.
How does DAS work?
DAS typically involves connecting storage devices, such as hard disk drives (HDDs) or solid-state drives (SSDs), directly to the host system using interfaces like Serial ATA (SATA), USB, Thunderbolt, or SCSI. The host system recognizes the attached storage devices as if they were internal drives, allowing for direct access and management of the storage resources.
Is DAS suitable for all types of storage requirements?
Direct Attached Storage is well-suited for various use cases, including personal computing, small businesses, or applications that require high-performance local storage. However, it may not be ideal for scenarios that involve shared access to storage resources or require scalability beyond the capacity of a single host system.
Can I expand or upgrade a DAS configuration?
Yes, DAS configurations can often be expanded or upgraded by adding more storage devices to the host system or connecting additional external storage arrays. However, the scalability of DAS is limited to the capacity and connectivity options supported by the host system.
Can DAS be used in conjunction with networked storage solutions?
Yes, it is possible to combine DAS with networked storage solutions like SAN or NAS. This hybrid approach allows for leveraging the benefits of both DAS (such as high performance and direct access) and networked storage (such as centralized management and shared access) in a single infrastructure.