When your USB flash drive is not showing up in File Explorer after being plugged in, it’s a common and frustrating issue. The drive might be missing entirely, show up briefly and then disappear, or not be detected at all. This prevents access to important files stored on the device.
When a flash drive is not showing up, rushing into fixes without knowing the cause can risk permanent data loss. This guide outlines safe steps to diagnose the issue on Windows or Mac, explains common reasons a USB isn’t detected, and helps determine when to seek professional data recovery support.
Step 1: Perform These Initial Safe Checks
Before assuming major drive failure, rule out simple external issues. These apply whether your flash drive is not detected, not showing up, or simply not working correctly.
(H3) 1. Check Physical Connections: Port and Drive Seating
Check Physical Connections: Port and Drive Seating
A secure connection is vital.
- Reseat the Drive: Unplug the flash drive and firmly plug it back in. Ensure it’s fully seated in the USB port.
- Try a Different USB Port: The port you’re using might be faulty or unpowered. Try connecting the drive to a different USB port on your computer, preferably one directly on the motherboard (often on the back of desktops). Avoid passive USB hubs if possible.
- Check for Debris: Look inside the USB port on the computer and the drive’s connector for any obvious lint or debris that might be obstructing the connection. Use compressed air carefully if needed.
Test on a Completely Different Computer
- Connect Elsewhere: Plug the flash drive into another known-working computer (Windows or Mac).
- Interpret Results:
- Works on Second Computer: If the drive is detected and accessible on another machine, the issue likely lies with your original computer (USB drivers, OS settings, conflicting software, or faulty ports). The problem isn’t the drive itself.
- Still Not Showing Up: If the drive also fails to appear or work on a second (or even third) computer, the problem is almost certainly within the flash drive itself (controller failure, NAND issue, internal connection break, severe corruption).
Examine for Physical Damage
Look closely at the flash drive itself.
- Is the USB connector bent, loose, or damaged?
- Is the casing cracked or broken?
- Was the drive recently dropped or exposed to liquid?
If visible physical damage exists, do not attempt to force it into a port or perform DIY repairs. Proceed directly to seeking professional help. For details on physical issues, read our guide on recovering data from broken flash drives.
Critical Point: If these initial checks fail to make the drive appear, or if you noticed any strange behavior before it stopped showing up (errors, sluggishness) or there’s physical damage, STOP. Do not proceed with software utilities or commands. Further attempts could cause irreversible data loss.
Why Isn't My USB Flash Drive Showing Up
A USB flash drive not showing up or not detected can be due to faulty USB ports/cables, driver issues, or incorrect formatting. More severe causes include file system corruption (drive appears RAW/unallocated), NAND flash memory degradation, controller chip failure, or physical damage to the drive’s PCB or connector.
Step 2: Checking Drive Status Within Your Operating System (Diagnosis ONLY)
If basic checks pass but flash drive not showing up in file browser, see if OS recognizes it at lower level. Warning: Use tools ONLY to view status. Do NOT Format, Initialize, Erase, or run repair commands if data recovery needed.
How to Check if Windows Detects the Flash Drive
Using Disk Management
This tool shows how Windows sees storage devices.
- How to Open: Right-click the Start button -> select “Disk Management”.
- What to Look For: Scan the list of disks. Look for a removable disk matching your flash drive’s size. Even if it’s not showing up in File Explorer, it might appear here.
- Shows Healthy but No Drive Letter: Sometimes simply assigning a drive letter resolves minor detection issues (Right-click partition -> Change Drive Letter and Paths -> Add). Use caution if you suspect drive failure.
- Shows “RAW” or “Unallocated”: Windows sees the hardware but not a valid file system. Indicates severe corruption or partition loss. DO NOT FORMAT.
- Shows “No Media”: The reader/port is seen, but no storage media is detected inside (severe internal issue).
- Shows “Unknown” / “Not Initialized”: Severe partition table issues or hardware problems. Windows might prompt to initialize (MBR/GPT). DO NOT INITIALIZE.
- Completely Absent: If the drive isn’t listed at all, it confirms a major detection failure (connection, power, or severe internal hardware failure).
Using Device Manager
This checks if the hardware component itself is recognized by Windows.
- How to Open: Right-click Start button -> select “Device Manager”.
- What to Look For: Expand “Disk drives,” “Portable Devices,” and “Universal Serial Bus controllers.” Look for your flash drive by name, as a “USB Mass Storage Device,” or any device with a yellow exclamation mark or down arrow.
- Meaning: An error icon often indicates a driver issue (potentially a symptom of hardware failure causing the drive not to work). If the drive is completely absent here and in Disk Management, it strongly points to a hardware problem.
How to Check if macOS Detects the Flash Drive
Using Disk Utility
- How to Open: Applications -> Utilities -> Disk Utility. Ensure ‘View’ -> ‘Show All Devices’ is selected.
- What to Look For: Check the left sidebar. Does the USB flash drive appear?
- Listed & Volume Mounted (Not Greyed Out): macOS detects and can access the file system. If not showing up in Finder, check Finder Preferences (General -> Show external disks; Sidebar -> Locations -> Show external disks).
- Listed but Volume Greyed Out (Unmounted): macOS sees the hardware, but cannot mount the volume, usually due to file system corruption or unsupported format. Do NOT use ‘Erase’ or ‘Partition’. Use ‘First Aid’ with extreme caution (see risks below).
- Listed as “Uninitialized” or No Volume Shown: Severe partition map or file system damage. Do NOT Initialize/Erase.
- Completely Absent: If the drive doesn’t appear at all, it indicates a significant connection, power, or internal hardware failure preventing detection.
Using System Information
Provides detailed hardware connection info.
- How to Open: Hold Option (⌥) key -> click Apple Menu () -> select “System Information…”.
- What to Look For: Check under “Hardware” -> “USB”. If your flash drive is listed, macOS recognizes the hardware connection, even if it’s not showing up elsewhere. If absent, it confirms a deeper detection issue.
Common Reasons Why Your Flash Drive Isn't Showing Up
- Faulty USB Port/Cable/Reader: Simple external factors ruled out by initial checks.
- Driver Issues (Less Common): Conflicts or corruption in system drivers preventing communication.
- File System Corruption (Common): Drive shows as RAW, needs formatting, or files are inaccessible due to damaged logical structure (often from improper removal). This is a major reason a drive is not recognized. Learn more about dealing with corrupted USB flash drives.
- Incorrect Formatting: Drive formatted with a file system the current OS doesn’t recognize.
- Partition Issues: Lost or damaged partition table making the drive not show up correctly.
- Hardware Failure (Common):
- Controller Chip Failure: The drive’s “brain” dies, making it completely unresponsive or showing incorrect size.
- NAND Memory Failure: Internal flash memory wears out or fails.
- Internal Connection Failure: Broken solder joints inside the drive.
- Physical Damage: Snapped connector, cracked PCB, water damage preventing the drive from working at all.

DIY Recovery
Risks permanent data loss
Let the Specialists Handle It
DIY attempts often result in permanent data loss. Our certified recovery specialists use advanced tools in controlled environments for the highest success rate.

24/7 Emergency Service
Why Common "Fixes" Destroy Data
Many online guides suggest using OS tools to “fix” undetected drives. These actions are designed to make the drive writable again, usually by ERASING existing data. Avoid them if recovery is your goal.
Formatting / Initializing / Erasing
NEVER DO THIS IF YOU NEED YOUR DATA. Agreeing to format, initialize, or erase when prompted by Windows or Mac essentially wipes the drive’s file map, making data recovery exponentially harder and often impossible with standard methods. This action doesn’t fix the reason the flash drive is not showing up, it just erases potential evidence.
CHKDSK (Windows) / Disk Utility First Aid (Mac)
These tools attempt file system repair. On failing drives (bad sectors, controller issues) or severely corrupted ones, they can misinterpret data, perform damaging “repairs,” cause the drive to fail completely under stress, or delete file fragments needed for recovery. Use only as a last resort AFTER data recovery or if data is not needed.
DIY Physical "Repairs"
Attempting to glue, bend, or solder broken physical parts yourself is extremely likely to cause further electrical damage and hinder professional recovery efforts for a drive that stopped working.
When is Professional Data Recovery Necessary?
If the safe initial checks fail and diagnostic tools show problems (or the drive isn’t detected at all), professional help is the recommended path, especially if:
- The drive is physically damaged.
- The drive prompts to be Formatted/Initialized/Erased (and contains needed data).
- The drive shows as RAW, Unallocated, No Media, or Uninitialized.
- The drive is completely undetected in Disk Management / Disk Utility / System Information.
- The drive contains critical, irreplaceable data.
- You have already tried DIY software unsuccessfully (further attempts risk more damage).
Unsure if recovery is generally possible? Our overview explains: Can Data Be Recovered From a USB Flash Drive?
Don't Let Data Loss Ruin Your Business
Minimize business disruption. We retrieve lost data fast, so you can focus on what matters.
The Professional Recovery Advantage (PITS Data Recovery)
PITS Data Recovery utilizes methods and tools far beyond DIY capabilities for drives that are not showing up or not working:
- Safe Drive Imaging: We create a clone first using specialized hardware to prevent further damage to your original drive.
- Advanced Logical Recovery: We use sophisticated software to bypass file system corruption and reconstruct data, even from RAW drives.
- Component-Level Repair: Our technicians can perform micro-soldering on PCBs if needed.
- Chip-Off Recovery: For severely damaged or unresponsive drives, we can perform NAND chip-off recovery.
- Expertise & Environment: We have the knowledge and controlled environments (including cleanrooms when necessary for complex repairs) to handle delicate flash media safely.
- Clear Process: We provide a detailed evaluation and quote before proceeding. Learn about our data recovery process.
Get a Free Consultation.
Our recovery experts are ready to assess your device and guide you through the safest path to recovery. Fill out the form to get started.
"*" indicates required fields
Recommended Actions If Your Flash Drive Isn't Detected
If your USB drive isn’t working correctly:
- Stop & Disconnect: Immediately stop trying to use the drive. Safely eject and remove it.
- Do Not Format/Repair: Avoid all formatting prompts and repair utilities.
- Do Not Attempt Physical Fixes: Don’t try to bend, glue, or solder broken parts.
- Gather Information: Note the drive model, the computer/OS used, error messages, and circumstances.
- Contact PITS Data Recovery: Reach out for a professional evaluation. Explain the symptoms accurately (e.g., “flash drive not showing up,” “not detected,” “stopped working”).
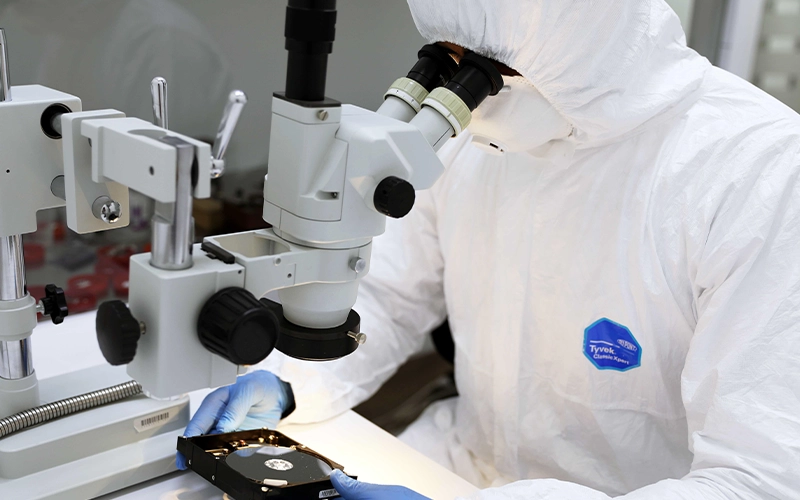

Conclusion: Prioritize Data Safety
A USB flash drive not showing up, working, or being detected indicates a potential failure. Using repair tools or formatting without proper diagnostics can lead to irreversible data loss. Perform safe checks, know the limits of DIY methods, and rely on experts. PITS Data Recovery specializes in recovering data from flash drives that aren’t showing up or recognized.