Overview
A client approached PITS Data Recovery after their 64GB monolithic USB flash drive failed without warning. The device was used for years as a primary storage unit for critical files and personal media. Unfortunately, the client had no backup and all of their documents, photos, and project files existed only on this single flash drive.
The drive no longer registered on any computer, showing no power indicator or mounting behavior. It held priceless data including high-resolution travel photos, academic research, and sensitive financial records. The urgency and severity of the case were clear.
Device Summary
- Type: USB 2.0 Monolithic Flash Drive
- Capacity: 64GB
- File System: FAT32
- Symptoms: Dead drive, no detection, no LED activity, no system response
- Backup Available: No
Initial Evaluation
The device had no external damage, but the lack of system response indicated internal controller failure or damaged data lines within the monolithic chip. These chips do not have visible components or accessible solder joints, so we classified it as a non-standard monolithic flash memory recovery.
Our recovery protocol required direct chip-level access through advanced diagnostic and microelectronic techniques.
Get a Free Consultation.
Our recovery experts are ready to assess your device and guide you through the safest path to recovery. Fill out the form to get started.
"*" indicates required fields
Recovery Process
Step 1: Non-Destructive Imaging and Internal Assessment
We began by performing X-ray scanning microscopy to visualize the internal structure of the monolithic chip. This allowed our engineers to:
- Confirm chip orientation
- Identify controller-to-NAND signal pathways
- Assess for internal fractures or layer separation
This non-invasive step guided safe encapsulant removal and solder pad exposure.
Step 2: Resin Removal and Microscopic Surface Cleaning
The chip was de-encapsulated using a controlled thermal and chemical process that exposed its signal pads without damaging the substrate. Surface cleaning was done under high-magnification optical microscopes to eliminate resin residues and oxidation.
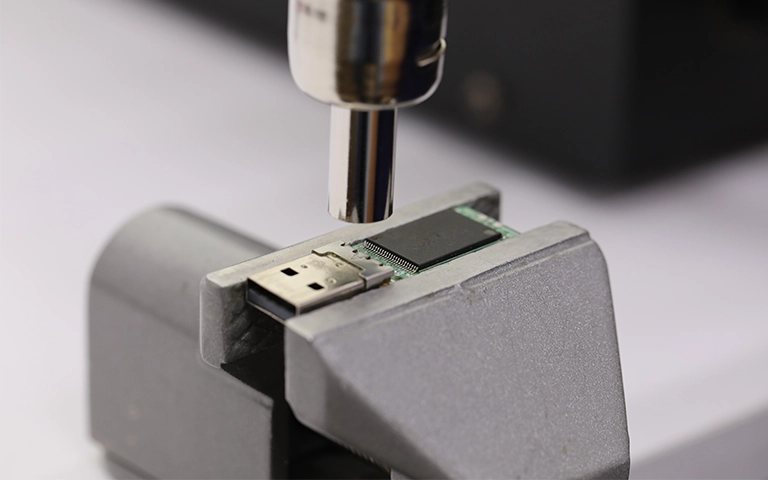

Step 3: Pinout Mapping with Logic Analyzer
Since the chip model was undocumented and not present in our internal pinout database, we used a logic analyzer to probe the exposed pads dynamically. This step helped identify:
- Power and ground lines
- Command and control signals (RE, WE, CLE, ALE)
- Data I/O channels
The analyzer allowed us to validate signal integrity and isolate functional lines for NAND communication.
Step 4: Precision Soldering with JBC Microsoldering Equipment
Once the pad layout was confirmed, we used JBC ultra-fine soldering stations with custom-tipped irons and micro-wire to bond connection wires directly to the NAND interface points.
Our JBC platform provided:
- Ultra-stable temperature regulation
- Micron-level soldering precision
- Anti-static handling for safe NAND work
Each wire was verified under a stereo microscope before interfacing with the NAND reader.
Step 5: NAND Imaging and Dump
Using our NAND reader, we powered the chip externally and initiated a full binary dump. Multiple passes were conducted to reduce ECC interference and ensure completeness.
We then extracted raw data blocks containing fragmented files, metadata tables, and directory structures.

Step 6: Data Reconstruction
Raw dumps from monolithic chips are often scrambled due to controller-level wear leveling and translation tables. Our engineers reconstructed the original file system by:
- Identifying XOR patterns
- Rebuilding FAT tables and directory trees
- Correcting corrupted block maps
- Validating file headers for media and document types
Your Data Security Is Our Priority
Data privacy isn’t optional. It’s our commitment. Our secure recovery process ensures your sensitive information stays protected from start to finish.
HIPAA Compliant
GDPR Compliant
Secure Facility
NDA Available
Trust in certified security. Start your recovery today! Call Now: 888.611.0737
Results
After three days of advanced recovery work, we achieved:
- 98.3% recovery success
- Over 8,000 files restored, including
- JPG, PNG, and BMP photos
- MP4 and AVI videos
- DOCX, XLSX, PDF documents
- Archives and application data
- JPG, PNG, and BMP photos
- Original folder structure and file naming preserved
- Delivery to the client on an encrypted, verified USB SSD
Client Outcome
The client verified the recovered files remotely and was thrilled to find all their documents and personal photos restored. They had previously been told by a local repair shop that the device was unrecoverable.
This case highlights that even when consumer tools and diagnostics fail, expert labs equipped with logic analyzers, X-ray scanners, and precision microsoldering tools can achieve full recovery from monolithic flash devices.
Lessons and Best Practices
- Monolithic flash drives cannot be repaired or accessed with traditional methods. Recovery requires invasive and high-risk procedures, which must be handled by specialists.
- No backup = high-risk. Flash media, especially monolithic types, can fail instantly and unpredictably.
- Do not open or tamper with failed drives. Attempting DIY disassembly can permanently damage internal wiring or the memory layer.
- Act quickly. The sooner the device is isolated and evaluated, the better the outcome.
Conclusion
This case demonstrates the advanced methods used by PITS Data Recovery in flash drive recovery to restore data from completely failed monolithic flash drives even when no backup is available and the chip is undocumented.
By using X-ray imaging, logic analyzers, and JBC precision soldering, our engineers were able to reverse-engineer the chip, extract the raw NAND content, and rebuild the data from scratch.
If your USB flash drive or microSD card has failed and contains irreplaceable data, contact us today. Our lab is equipped to handle even the most complex monolithic recovery cases with care and confidentiality.
Don't Let Data Loss Ruin Your Business
Minimize business disruption. We retrieve lost data fast, so you can focus on what matters.