A Redundant Array of Independent Disks is a term for a storage system that shares and replicates data across multiple hard drives. RAID provides increased data reliability or I/O performance, although one goal may compromise the other. This system is used by businesses and individuals all over the world, as they rely on this secure media.
There are different RAID levels created to meet the various needs of the user. RAID 10 is considered one of the most widespread RAID configurations.
What is RAID 10? RAID 10 Explained
RAID 10 is designed based on the idea that data is striped across two sets. Consequently, this set consists of two disks with a mirroring system. This structure provides its users with security and reliability. If anything happens to one drive, its data is stored on the mirror drive.
RAID 10 is a combination of RAID 0 and RAID 1. This appliance provides more functionality due to the 1+0 merge. In RAID 10, RAID 1 system is responsible for copying data from one drive to the other, mirroring, and providing the user with fault tolerance and protection.
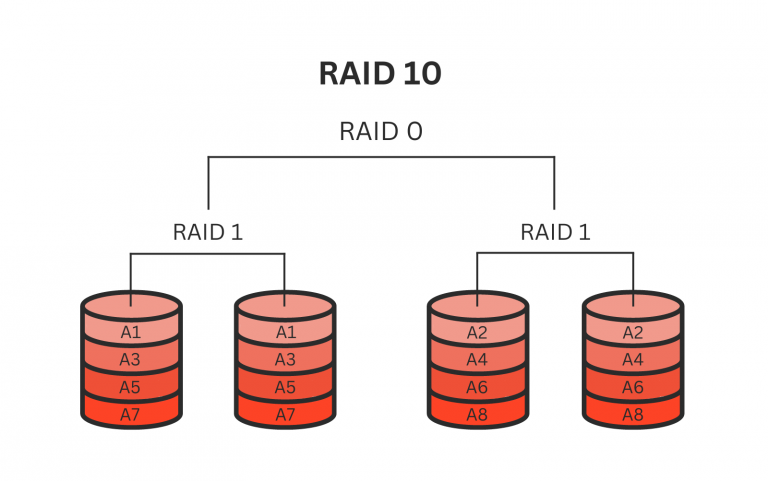
RAID 0, on the other hand, does not offer the security of the data. Nevertheless, it delivers enhanced access performance by spreading the data across two or more drives. This way, data is written simultaneously, which makes the storage process much faster.
Advantages of RAID Level 10:
- High Data Protection
- Redundancy
- Data Recovery
Disadvantages of RAID 10 Configuration:
- Maintenance Cost
- Risk of Data Loss
- Half of the Storage Usable
It may be costly to maintain due to the minimum four disks structure. And mainly because of this system, RAID 10 provides users with high performance and little to no downtime.
RAID 10 Configurations
There are multiple methods for applying RAID 10, each with benefits and factors to consider. Below are a few typical configurations of RAID 10:
Full Stripe RAID 10
In a Full Stripe RAID 10 configuration, data is striped across multiple mirrored sets of drives. It represents that data is both mirrored for redundancy and striped for improved performance. This structure requires a minimum of four drives, and data is divided into blocks that are then mirrored and striped. Full Stripe RAID 10 provides exceptional read and write performance, as it can use mirroring and striping. Nevertheless, it is more storage-intensive than other RAID 10 configurations.
Near vs. Far RAID 10
Near and Far RAID 10 configurations specify how data is mirrored and striped across drives.
Near RAID 10
In a Near RAID 10 setup, data is mirrored first, and then the mirrored pairs are striped. This structure offers exceptional redundancy, as two copies of data are maintained (one on each mirrored pair), and good performance. Near RAID 10 is a suitable choice for applications that prioritize maintaining data integrity.
Far RAID 10
In contrast, Far RAID 10 stripes data first and then mirrors it. This results in higher performance compared to Near RAID 10 but with slightly reduced redundancy. It is suitable for applications where performance is vital, and redundancy may be compromised somewhat.
Deciding on either Near or Far RAID 10 relies on individual requirements, finding the right balance between performance and redundancy.

Nested RAID 10
Nested RAID 10 configurations combine RAID 0 and RAID 1 arrays in various ways. For example, you can have a RAID 0 stripe of multiple RAID 1 mirrors.
Nested RAID 10 allows customized solutions that meet precise performance, capacity, and redundancy requirements. Nevertheless, establishing and managing it can be challenging.
Hybrid RAID 10
Hybrid RAID 10 configurations incorporate different drive technologies, such as Solid-State Drives (SSDs) and Hard Disk Drives (HDDs), into the same array. This method offers a budget-friendly solution for utilizing the high speed of SSDs for frequently accessed data while employing HDDs to store large amounts of data and ensure redundancy. Implementing a Hybrid RAID 10 configuration requires strategic consideration for selecting and arranging the different types of drives within the array.
Flex RAID 10
Flex RAID 10 is a dynamic configuration that permits adding or removing drives without disrupting the array’s operation. This level of flexibility proves especially valuable regarding scalability and maintenance. However, it necessitates using a RAID controller that is compatible with these functionalities.
Selecting the appropriate RAID 10 configuration relies on the distinct requirements of your organization, encompassing performance, redundancy, scalability, and cost. Each setup entails compromises, necessitating thoughtful evaluation of your data storage needs before deploying.
RAID 10 vs. RAID 5 - What is The Difference?
RAID level 10 is often compared with RAID 5 configuration. Both of these symptoms provide users with a reliable way to store data. Nevertheless, the operation within this system is different.
RAID 5 vs RAID 10 have a different system for storing data. While RAID 5 divides the data equally to multiple disks, RAID level 10 mirrors it and holds it on another drive. This way, RAID 10 offers better data security to its users.
The minimum disk requirement for a RAID 5 system is 3. Due to the mirroring storage system, minimum drives for RAID 10 should be even, so the number of disks is minimum 4. However, RAID 10 array provides a slower speed and less storage compared to RAID 5.
Hence, if you need fast and high storage capacity, it is preferable to use RAID 5. However, if the security of your data is a priority for you, then employing RAID 10 is beneficial.
RAID 10 Failure and Data Loss
RAID 10 is a reliable data storage device that provides users with high data security and prevents complete data loss. However, this system works only when functioning without any faults. When there is some damage to the RAID array 10, files’ inaccessibility can be unavoidable.
As we mentioned before, RAID level 10 has a mirroring system. Hence, if one of the disk fails, the data can be successfully restored from the other drive. However, if both drives with valuable data fail, then there are severe problems a user has to deal with.
Recovering data from RAID 10 is a complicated process that requires years of experience. Only a reputable data recovery company specializing in RAID recovery can help you with such a problem. Moreover, entrusting your valuable data to reliable providers is preferable in a data loss situation.
Advantages of Working with Us
PITS Global Data Recovery Services is a dependable company that provides businesses and individuals with RAID 10 data recovery. Our engineers have deep knowledge of RAID systems and can restore lost, corrupted, or deleted data from all RAID levels.
By performing a risk-free evaluation at the beginning of our recovery process, we thoroughly inspect the device to understand what happened. This way, our engineers find the reason for data loss and level of damage. We select the most suitable data recovery strategy for the device based on the evaluation results.
Our next step is to safely and successfully restore access to the data. Our technicians work on RAID devices only in ISO Certified Class 10 Cleanroom to perform the recovery with the highest level of security of your device and data. Working in a controlled environment, our engineers ensure that no dirt, humidity, or dust can damage your RAID array.
PITS Global Data Recovery Services has years of experience in the data recovery industry and is proud to support a 99% success rate. Our aim is to provide our customers with a positive experience, a safe process, and maximum results. Become our other successful case by starting your RAID 10 data recovery with us today.
You can get in touch with us by calling our customer service line or filling out the request help form below. Our expert team will gladly answer all your questions and provide you with all the required information.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does RAID 10 stand for?
RAID 10 stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disks 10. It is a combination of RAID 1 (mirroring) and RAID 0 (striping) technologies.
How does RAID 10 work?
RAID 10 combines the benefits of mirroring and striping. It requires at least four drives, which are divided into two sets. The data is mirrored between the drives in one set (RAID 1), providing redundancy, and then the mirrored sets are striped (RAID 0) to improve performance.
In which scenarios is RAID 10 recommended?
RAID 10 is well-suited for environments that require both high performance and data redundancy. It is commonly used in database servers, file servers, and other applications with a heavy emphasis on data reliability and speed.
Can I convert an existing RAID setup to RAID 10?
Converting an existing RAID setup to RAID 10 typically requires backing up the data, reconfiguring the drives, and then restoring the data onto the new RAID 10 array. It is recommended to consult the documentation or seek assistance from a professional to ensure a smooth transition and minimize data loss risks.
Can I mix drive sizes in a RAID 10 array?
While it is technically possible to mix drive sizes in a RAID 10 array, it is generally not recommended. Mixing drive sizes can lead to suboptimal performance, reduced usable capacity, and potential compatibility issues. It is best to use drives of the same size and model for optimal results.
Is RAID 10 a replacement for regular data backups?
No, RAID 10 should not be considered a substitute for regular data backups. RAID 10 provides fault tolerance and improved performance, but it does not protect against data loss from events such as accidental deletion, file corruption, or disasters. Regular backups are essential to ensure data can be restored in case of catastrophic failures or human errors.