When it comes to data storage systems, there are two main options: JBOD and RAID. Both JBOD and RAID have their advantages and disadvantages, and it is essential to consider the differences between them to make an informed decision about which is right for you.
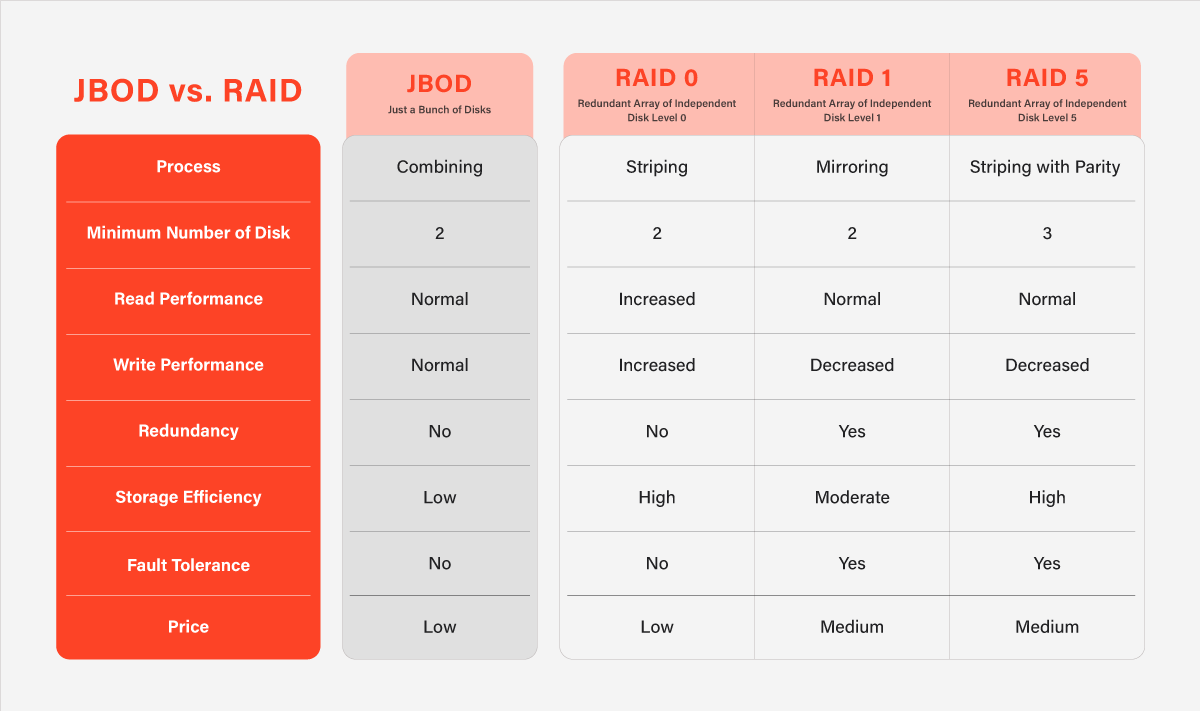
JBOD, which stands for “just a bunch of disks,” is considered a popular storage option. As the name suggests, it is a collection of hard drives treated as independent storage units. RAID, on the other hand, stands for “redundant array of independent disks.” RAID uses multiple hard drives to provide redundancy and improve performance.
In this blog, our team will examine the differences between JBOD and RAID and the various RAID levels.
JBOD vs. RAID 0
RAID 0 is often compared to JBOD because it uses multiple hard drives as a single storage unit. However, RAID 0 uses striping, which divides data across multiple drives. This improves performance, but it does not provide any redundancy.
In contrast, JBOD presents each hard drive as a separate storage unit. This means that if one hard disk fails, you will lose all the data on that drive, but the other drives will be unaffected.
The advantage of RAID 0 is that it provides faster read and write speeds than JBOD. However, the downside is that if one drive fails, you will lose access to all the data on the drives. For this reason, when choosing between RAID 0 vs. JBOD, RAID 0 is generally only recommended for situations where speed is more important than data redundancy, such as video editing or gaming.
JBOD vs. RAID 1
RAID 1 is a much safer option than RAID 0 because it provides data redundancy.
In a RAID 1 configuration, two drives are used, and data is mirrored between them. If one drive fails, you still have a complete copy of all your data on the other drive.
On the other hand, JBOD (Just a Bunch of Disks) offers no redundancy. All the data on JBOD is lost.

The advantage of RAID 1 is that it provides complete data redundancy. However, the downside is that it requires twice as many hard drives as JBOD to store the same amount of data.
Additionally, read and write speeds are slower in RAID 1 because data has to be written to both drives. Hence, when choosing between RAID 1 vs. JBOD, it is essential to evaluate your storage needs fairly.
JBOD vs. RAID 5
RAID 5 is a more complex configuration than RAID 1, but it offers better performance and data redundancy. In a RAID 5 configuration, three or more drives are used, and data is divided across all the drives in the array. Parity data is also stored on each drive, which allows the system to recover data if one drive fails.
JBOD, as previously mentioned, offers no data redundancy. If one drive fails, data is irreversibly lost.
The advantage of RAID 5 is that it offers good performance and data redundancy, making it a good choice for servers or other situations where data availability is critical. However, it requires at least three drives, and read and write speeds are slower than in RAID 0. You must consider all your storage requirements when choosing between RAID 5 vs. JBOD.
Which Storage Option to Choose: JBOD vs. RAID 0 vs. RAID 1 vs. RAID 5
JBOD and RAID offer different benefits and drawbacks. JBOD is a simple and inexpensive option, but it offers no data redundancy. RAID, on the other hand, provides data redundancy and improved performance, but it requires more hardware and is more complex to set up.
JBOD is a good choice if you are looking for a simple and inexpensive storage solution and do not need data redundancy. However, if you must ensure that your data is always available and do not mind the additional hardware and complexity, RAID is the better option.

When choosing a RAID array, consider your specific needs. RAID 0 is good for speed but offers no data redundancy.
RAID 1 provides complete data redundancy but requires twice as many hard drives as JBOD.
RAID 5 offers good performance and data redundancy but requires at least three drives and has slower read and write speeds than RAID 0.
It is also critical to note that there are other RAID configurations, such as RAID 6, RAID 10, and RAID 50, which offer varying levels of performance and data redundancy. However, these configurations are generally more complex and require more hardware than the configurations we’ve discussed.
Ultimately, the choice between the JBOD array and RAID, as well as the specific RAID configuration, depends on your particular needs and budget. If you are not sure which system is right for you, it is a good idea to consult a data storage expert who can help you make an informed decision.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is JBOD faster than RAID 5?
JBOD and RAID 5 exhibit distinct performance attributes. Generally, RAID 5 outperforms JBOD regarding read operations due to its ability to distribute data across multiple disks, enabling parallel access. However, in certain scenarios, JBOD may offer superior write operation speed as it does not involve the parity calculations inherent to RAID 5. When selecting between the two, it is crucial to consider your unique use case and performance needs.
What is better, JBOD or RAID 0?
JBOD and RAID 0 (striping) superiority depends on individual requirements. RAID 0 enhances performance by distributing data across multiple disks but lacks redundancy. Conversely, JBOD merely combines disks without any performance advantages or redundancy. If you want to achieve higher performance and effectively manage the data loss risk, RAID 0 may be a suitable choice. Alternatively, JBOD may be the preferred choice if prioritizing data integrity and fault tolerance.
How is RAID different from JBOD?
RAID and JBOD are fundamentally different storage configurations. Depending on the RAID level, RAID involves combining multiple disks into an array to provide redundancy, improved performance, or both. On the other hand, JBOD connects disks without any redundancy or performance enhancement. Each disk in a JBOD appears as a separate drive to the operating system.
Should I use RAID or JBOD for backup?
Your choice between RAID and JBOD for backup relies on your backup strategy and priorities. RAID can provide data redundancy and enhanced performance, making it a superior option if you require both backup and high availability. RAID configurations like RAID 1 (mirroring) or RAID 5 (striping with parity) can safeguard against disk failures. While JBOD is not typically used for backup due to its absence of redundancy, it can be a viable alternative if you have a distinct backup strategy, such as offsite backups or regular data replication. Ultimately, the decision should align with your specific backup requirements and budget.